Home > High Tensile steel
High Tensile steel
Introduction
High tensile steels are engineered for applications that require superior strength, durability, and resistance to mechanical stress. Among the most commonly used high tensile steels are 4140, 4340, and P20. These metals are valued in various industries for their robust mechanical properties and versatility, particularly in pre-hardened conditions.
Product Images
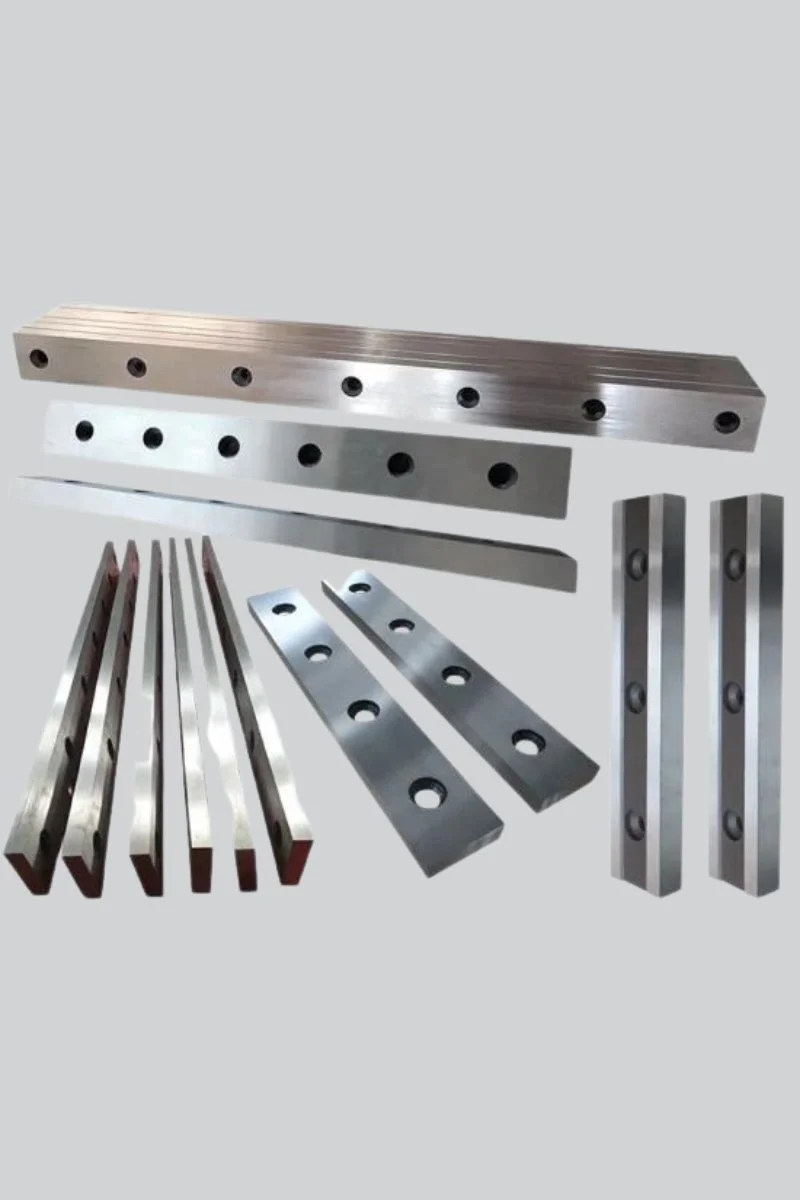
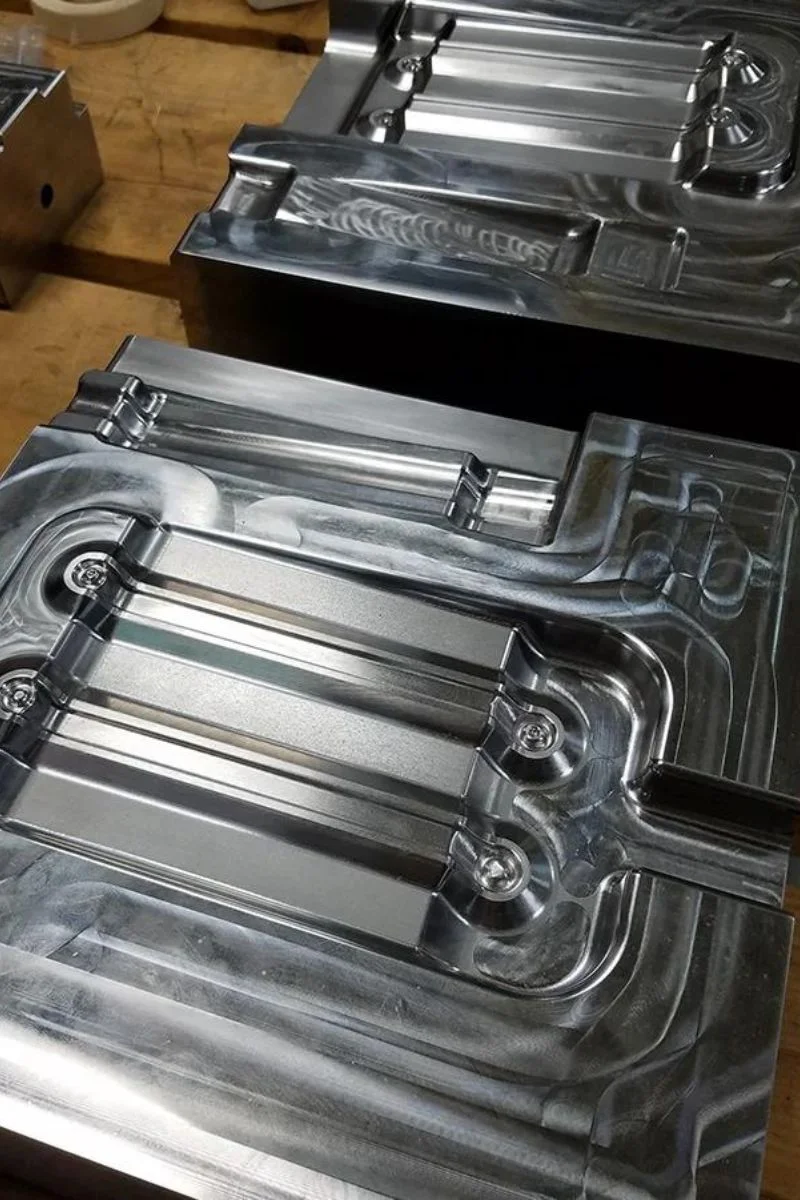
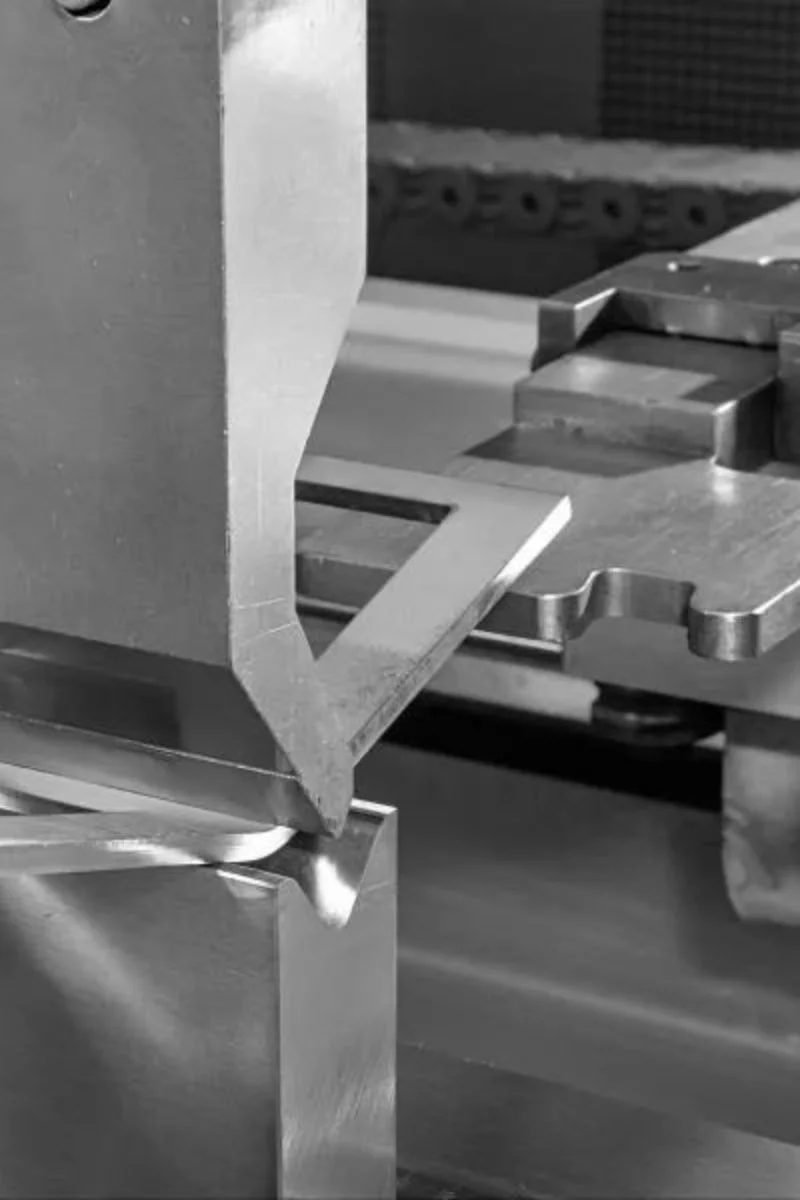




4140 Steel
4140 steel is a chromium-molybdenum alloy steel known for its excellent hardness, strength, and wear resistance. It is often used in applications where toughness and high fatigue strength are crucial.
- Hardness: 28-32 HRC (pre-hardened)
- Tensile Strength: 655 MPa (95,000 psi)
- Yield Strength: 415 MPa (60,000 psi)
- Elongation: 25%
- Impact Resistance: Good
- Powder Compacting Tools: Pressing dies for powder metallurgy.
Applications
- Automotive Components: Crankshafts, gears, and axle shafts.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Drilling collars and tool joints.
- Machinery Parts: High-stress gears, shafts, and spindles.
P20 Steel
P20 steel is a versatile mold steel with moderate strength and good machinability. It is commonly used in the plastic molding industry and for die-casting applications.
Key Properties:
- Hardness: 28-32 HRC (pre-hardened)
- Tensile Strength: 930 MPa (135,000 psi)
- Yield Strength: 830 MPa (120,000 psi)
- Elongation: 20%
- Machinability: Good
Applications
- Plastic Injection Molds: For manufacturing plastic components.
- Die-Casting Dies: Used in the production of aluminum, zinc, and magnesium parts.
- Tooling: Bases and holders for various machining operations.
4340 Steel
4340 steel is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy steel that offers high strength and toughness. It is well-suited for heavy-duty applications where high fatigue strength and impact resistance are required.
Key Properties:
- Hardness: 30-36 HRC (pre-hardened)
- Tensile Strength: 745 MPa (108,000 psi)
- Yield Strength: 470 MPa (68,000 psi)
- Elongation: 18%
- Machinability: Excellent
Applications
- Aerospace Industry: Landing gear, bolts, and other structural components.
- Military: Armor plating and high-strength vehicle components.
- Heavy Machinery: Drive shafts, connecting rods, and other critical parts.
High tensile steels such as 4140, 4340, and P20 offer a range of mechanical properties that make them ideal for demanding applications across different industries. Their combination of hardness, strength, and toughness ensures reliable performance and longevity, particularly in pre-hardened conditions. By understanding the specific properties and applications of each of these steels, engineers and manufacturers can select the most appropriate material for their needs, ensuring optimal performance and durability in their products.
